
Nutrition and healthy eating habits play a fundamental role in maintaining overall health and well-being. The foods we consume provide the nutrients, vitamins and minerals our bodies need to function optimally. This article explores the benefits of a balanced diet and the importance of nutrition and healthy eating. By understanding the importance of nutrition and adopting healthy eating habits, individuals can improve their overall health. So they can improve their quality of life.
1. The Benefits of a Balanced Diet
Essential Nutrients:
- Macronutrients: Carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are the body’s primary energy sources and are essential for growth, repair, and various physiological functions.
- Micronutrients: Vitamins and minerals are essential for maintaining overall health, supporting immune function, and promoting the proper functioning of organs and systems.
Energy Balance:
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: A balanced diet helps individuals achieve and maintain a healthy body weight, reducing the risk of obesity and related health conditions.
- Optimal Energy Levels: Consuming the right amount of nutrients provides the energy needed for daily activities, promoting vitality and productivity.
Improved Physical Function:
- Enhanced Muscle Function: Adequate protein intake supports muscle growth, repair, and maintenance, contributing to strength and physical performance.
- Bone Health: Consuming sufficient calcium and vitamin D supports bone health, reducing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures.
2. The Impact of Different Food Groups in Healthy Eating
Fruits and Vegetables:
- Nutrient Density: Fruits and vegetables are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, promoting overall health and reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
- Fiber Content: High-fiber fruits and vegetables support digestive health, maintain bowel regularity, and contribute to a feeling of fullness.
Whole Grains:
- Complex Carbohydrates: Whole grains provide a steady release of energy, fiber, and essential nutrients, promoting satiety and supporting digestive health.
- Heart Health: Whole grains can lower the risk of heart disease by reducing cholesterol levels. and promoting healthy blood pressure.
Lean Proteins:
- Muscle Maintenance: Lean protein sources, such as poultry, fish, legumes, and tofu, support muscle growth. repair, and maintenance.
- Satiety and Weight Management: Protein-rich foods help promote feelings of fullness, reducing excessive calorie intake and aiding in weight management.
Healthy Fats:
- Essential Fatty Acids: Healthy fats, such as those found in nuts, seeds, avocados, and fatty fish. They are important for brain function, hormone regulation, and cell health.
- Heart Health: Consuming unsaturated fats in moderation can help lower cholesterol levels. and reduce the risk of heart disease.
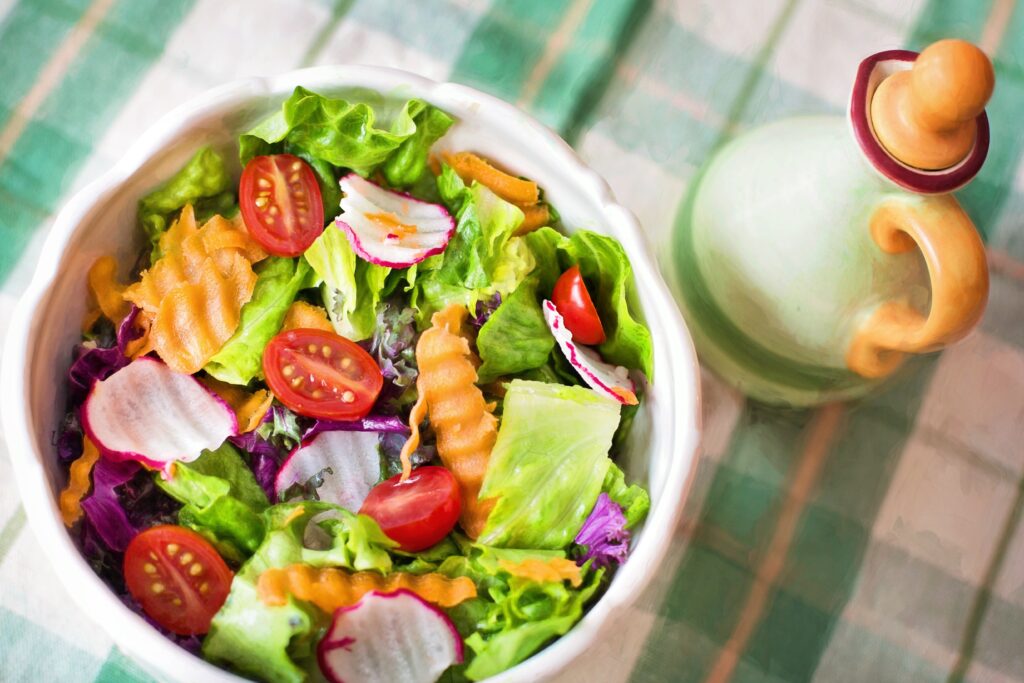
3. Making Healthier Food Choices
Portion Control:
- Mindful Eating: Paying attention to hunger and fullness cues can prevent overeating and promote a balanced intake of nutrients.
- Plate Method: Dividing the plate into appropriate portions of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins helps create a balanced meal.
Reading Food Labels:
- Understanding Nutritional Information: Reading food labels helps identify the nutritional content of packaged foods, enabling informed food choices.
- Ingredient List: Checking the ingredient list allows individuals to be aware of added sugars, unhealthy fats, and other potentially harmful additives.
Meal Planning and Preparation:
- Planning Ahead: Preparing a weekly meal plan and grocery list can help individuals make healthier food choices and avoid impulsive, less nutritious options.
- Cooking at Home: Preparing meals at home allows individuals to control ingredients, portion sizes, and cooking methods, ensuring healthier eating habits.
4. Nutrition and Disease Prevention
Cardiovascular Health:
- Heart-Healthy Eating: A balanced diet low in saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium can reduce the risk of heart disease and related conditions.
- Blood Pressure Management: Consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins helps maintain healthy blood pressure levels.
Type 2 Diabetes:
- Blood Sugar Control: A balanced diet with controlled carbohydrate intake, high in fiber, and low in processed sugars, helps regulate blood sugar levels. and reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight through proper nutrition and regular physical activity reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Cancer Prevention:
- Antioxidant-Rich Foods: Consuming a variety of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides antioxidants that help protect cells from damage. and reduce the risk of certain cancers.
- Fiber Intake: High-fiber diets, primarily from plant-based foods, are associated with a lower risk of colorectal cancer.
Nourishing the Body for Optimal Health
Nutrition and healthy eating habits are integral to maintaining optimal health and preventing chronic diseases. A balanced diet provides the body with the nutrients and energy it needs to function optimally. For example, a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins and healthy fats.
Individuals should make conscious food choices and practice portion control. They can improve their physical health by understanding the impact of different food groups. They can increase energy levels and support disease prevention.
Adopting healthy eating habits as a lifelong commitment contributes to overall health, longevity, and higher quality of life. It is necessary to prioritize nutrition and develop a positive relationship with food. It is important to view food as a tool to nourish the body, promoting a healthier lifestyle.
[…] mother and baby health. Every individual’s needs are different. It is important to follow the nutritional plan recommended by your individual healthcare professional during pregnancy. It should not be forgotten […]
[…] Nutrition is important for maintaining brain health. Nutrients such as antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids and B vitamins support brain function and protect brain health. Consuming brain-friendly foods such as fish, nuts, fruits and vegetables can support brain health. […]