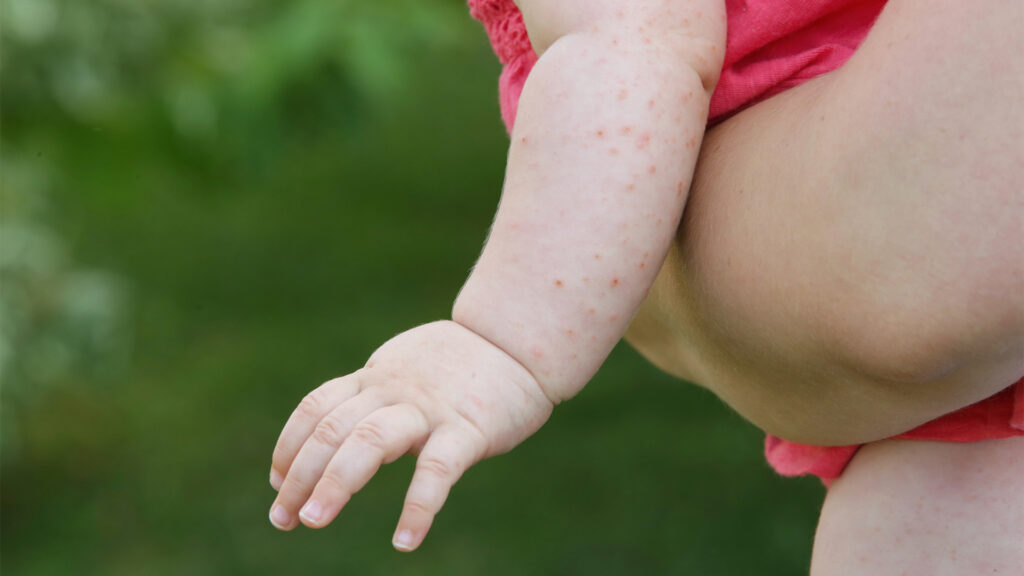
Scarlet fever is among the many diseases that affect children’s health. It is a contagious viral infection usually seen in children. This disease usually presents with symptoms such as red rash, fever and sore throat. However, there is an effective method of protection against this disease: vaccination.
What is Scarlet Fever?
The scarlet fever vaccine is a vaccine that protects against the scarlet fever virus. This vaccine is usually included in the routine vaccination schedule during childhood. Children usually receive the first dose in two doses, with the first dose around 1 year of age and the second dose between 4 and 6 years of age.
Benefits of Vaccination
- Reduces the Severity of the Disease: The vaccine reduces the severity of the disease. Vaccinated children tend to experience milder symptoms, even if they do get scarlet fever.
- Prevents Complications: The disease sometimes causes serious complications such as ear infections, pneumonia and brain inflammation. Vaccination reduces the risk of such complications.
- Creates Community Immunity: Vaccinated individuals create community immunity by preventing the spread of the disease. This also protects individuals who cannot be vaccinated.
Situations Where Vaccination Is Not Given
In some cases, children may not be vaccinated against scarlet fever. These situations may include:
- Allergy History: Children with a history of serious allergy to vaccines may not receive the vaccine.
- Immune System Problems: Children with a weak immune system may be more sensitive to vaccination.
- Pregnancy: This vaccine is generally not recommended during pregnancy. Therefore, pregnant mothers should have their children vaccinated after birth.
Prevention Ways
There are some precautions that can be taken to prevent scarlet fever for children who are not vaccinated:
- Complying with Hygiene Rules: It is important to comply with hygiene rules such as washing hands frequently and covering mouth and nose when coughing and sneezing. These prevent the spread of scarlet fever and other infectious diseases.
- Avoiding Contact with Sick People: Avoiding contact with people showing symptoms of scarlet fever reduces the risk of transmission.
- Contributing to Community Immunity: Unvaccinated children play an important role in maintaining population immunity. Therefore, it is important to support herd immunity with vaccinated children.
The scarlet fever vaccine provides an effective way to protect the health of children. Regular administration of this vaccine protects children from scarlet fever and its potential complications. It also helps reduce transmission throughout the community. However, in all cases, the advice and guidance of a healthcare professional is important.